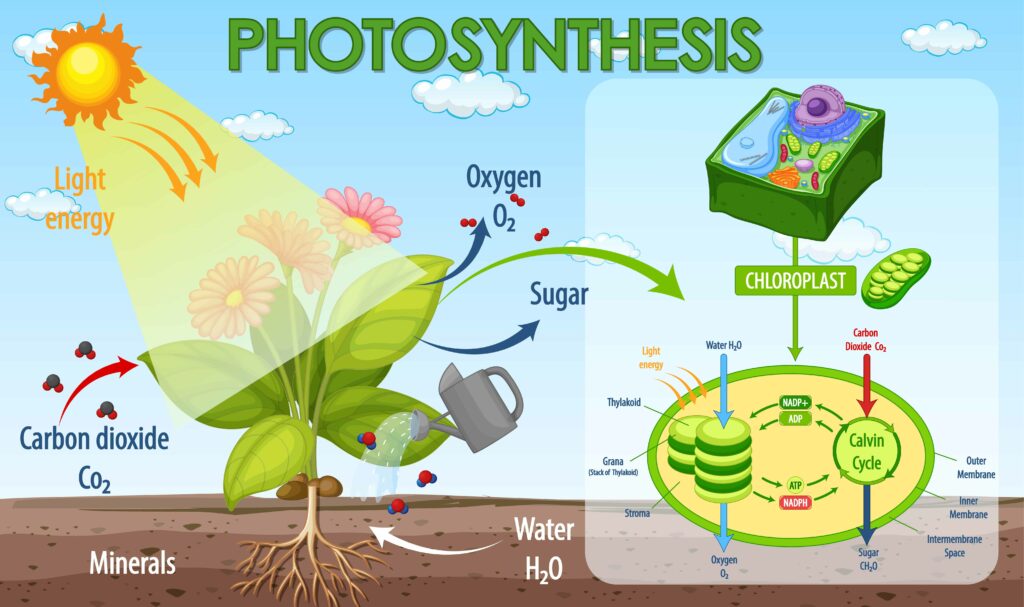
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism’s activities. In other words, The process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.
Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek phōs (φῶς), “light”, and sunthesis (σύνθεσις), “putting together”. This means “Combining together with the help of light.”
All green plants and a few other autotrophic organisms utilize photosynthesis to synthesize nutrients by using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. The by-product of the photosynthesis process is oxygen. Let us have a detailed look at the process, reaction, and importance of photosynthesis.
Where Does This Process Occur?
In plants, photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which contain the chlorophyll. Chloroplasts are surrounded by a double membrane and contain a third inner membrane, called the thylakoid membrane, that forms long folds within the organelle.
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Photosynthesis process requires several factors such as:
- Light Intensity: Without enough light, a plant cannot photosynthesise very quickly – even if there is plenty of water and carbon dioxide. Increasing the light intensity will boost the rate of photosynthesis.
- The concentration of CO2: Even if there is plenty of light, a plant cannot photosynthesise if there is insufficient carbon dioxide.
- Temperature: If it gets too cold, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease. Plants cannot photosynthesise if it gets too hot.
- Water: As water is an important factor in photosynthesis, its deficiency can lead to problems in the intake of carbon dioxide. The scarcity of water leads to the refusal of stomatal opening to retain the amount of water they have stored inside.
- Pollution: Industrial pollutants and other particulates may settle on the leaf surface. This can block the pores of stomata which makes it difficult to take in carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis Equation
The balanced equation for photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2. This means that the reactants, six carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules, are converted by light energy captured by chlorophyll (implied by the arrow) into a sugar molecule and six oxygen molecules, the products. The sugar is used by the organism, and the oxygen is released as a by-product.
Photosynthetic Pigments
- Photosynthetic organisms contain light-absorbing molecules called pigments. These photosynthetic pigments absorbs only specific wavelengths of visible light while reflecting others. The set of wavelengths absorbed by a pigment is its absorption spectrum.
- Different photosynthetic organisms have a variety of different pigments, so they can absorb energy from a wide range of wavelengths.
Types of Photosynthetic Pigments
- Chlorophyll
- Carotenoids
- Phycobilins
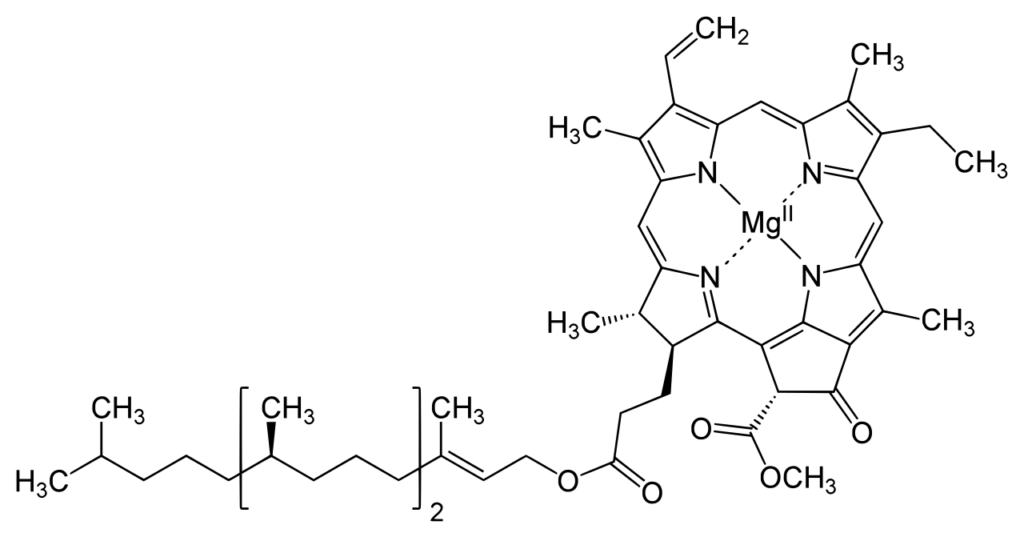
Structure Of Chlorophyll
The Steps of Photosynthesis/Process
The overall process of photosynthesis can be objectively divided into four steps/ process:
1. Absorption of light
- The first step in photosynthesis is the absorption of light by chlorophylls that are attached to the proteins in the thylakoids of chloroplasts.
- The light energy absorbed is then used to remove electrons from an electron donor like water, forming oxygen.
- The electrons are further transferred to a primary electron acceptor, quinine (Q) which is similar to CoQ in the electron transfer chain.
2. Electron Transfer
- The electrons are now further transferred from the primary electron acceptor through a chain of electron transfer molecules present in the thylakoid membrane to the final electron acceptor, which is usually NADP+.
- As the electrons are transferred through the membrane, protons are pumped out of the membrane, resulting in the proton gradient across the membrane.
3. Generation of ATP
- The movement of protons from the thylakoid lumen to the stroma through the F0F1 complex results in the generation of ATP from ADP and Pi.
- This step is identical to the step of the generation of ATP in the electron transport chain.
4. Carbon Fixation
- The NADP and ATP generated in steps 2 and 3 provide energy, and the electrons drive the process of reducing carbon into six-carbon sugar molecules.
- The first three steps of photosynthesis are directly dependent on light energy and are thus, called light reactions, whereas the reactions in this step are independent of light and thus are termed dark reactions.
Importance of Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis convert radiant or solar energy into chemical energy.
- Productivity of agricultural crops directly depends upon the rate of photosynthesis.
- It provides oxygen in atmosphere for all living organisms.
- It maintains the balanced level of oxygen and carbon dioxide ecosystem.
- It is the number one source of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- It contributes to the carbon cycle between the earth, the oceans, plants and animals.
- It contributes to the symbiotic relationship between plants, humans and animals.
- It directly or indirectly affects most life on Earth.
- It serves as the primary energy process for most trees and plants.
Site of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in special organelles known as chloroplast. This organelle has its own DNA, genes and hence can synthesize its own proteins. Chloroplasts consist of stroma, fluid, and stack of thylakoids known as grana. There are three important pigments present in the chloroplast that absorb light energy, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids.
Light Reactions of Photosynthesis
During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis (“light” reactions), chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which excites some electrons in the pigment molecules to higher energy levels; these leave the chlorophyll and pass along a series of molecules, generating formation of NADPH (an enzyme) and high-energy ATP molecules.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism’s activities. In other words, The process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.
Where Does This Process Occur?
In plants, photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which contain the chlorophyll. Chloroplasts are surrounded by a double membrane and contain a third inner membrane, called the thylakoid membrane, that forms long folds within the organelle.
What are the factors affecting photosynthesis?
The factors affecting photosynthesis are Light Intensity, The concentration of CO2, Temperature, Water, Pollution.
What are the types of Photosynthetic Pigments?
The types of Photosynthetic Pigments are Chlorophyll, Carotenoids, Phycobilins.
What are the steps to Process of Photosynthesis?
The steps to Process of Photosynthesis are Absorption of light, Electron Transfer, Generation of ATP and Carbon Fixation.
Why is photosynthesis important?
The importance of Photosynthesis are as follow:-
Photosynthesis convert radiant or solar energy into chemical energy.
Productivity of agricultural crops directly depends upon the rate of photosynthesis.
It provides oxygen in atmosphere for all living organisms.
It maintains the balanced level of oxygen and carbon dioxide ecosystem.