Venturi tube. Essential principle in engineering
VENTURI TUBE
It is a physical phenomenon with which procedures as diverse as the injection of fuel in a combustion engine, or the administration of the necessary proportion of oxygen in a respirator are carried out. It bears the name of its discoverer, the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi, and its operation has much to do with the Bernoulli Principle, another physicist, in this Swiss case, which roughly explains to us that throughout a duct, an ideal fluid (without viscosity or friction), keeps the same energy at all times
VENTURI TUBE
A Venturi tube is a device initially designed to measure the velocity of a fluid by taking advantage of the Venturi effect. Indeed, knowing the speed before the narrowing and measuring the pressure difference, the speed is easily found at the problem point.
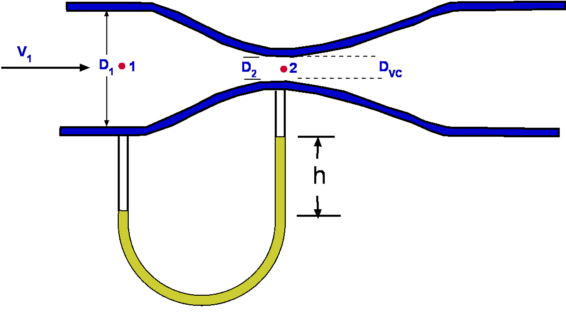
The classic application of speed measurement of a fluid consists of a tube formed by two conical sections joined by a narrow tube in which the fluid moves consequently at a higher speed. The pressure in the Venturi tube can be measured by a U-shaped vertical tube connecting the wide region and the narrow channel. The difference in liquid heights in the U-tube makes it possible to measure the pressure at both points and consequently the speed.
In other cases, it uses this effect to accelerate the velocity of a fluid by forcing it to pass through a narrow tube with the cone-shaped end. These models are used in numerous devices in which the speed of a fluid is important and are the basis of devices such as the carburetor
When using a Venturi tube, you have to take into account a phenomenon called. Cavitation This phenomenon occurs if the pressure in some section of the tube is less than the vapor pressure of the fluid. For this particular type of tube, the risk of cavitation is in the throat of the tube, since here, since the area is minimal and the velocity is maximum, the pressure is the lowest that can be found in the tube. When cavitation occurs, bubbles are generated locally, which travel along the tube. If these bubbles reach areas of higher pressure, they can collapse thus producing local pressure peaks with the potential risk of damaging the tube wall.
Venturi tube as flow meter.
The Venturi tube consists of a set of flanges and pipes with a convergent inlet cone and a divergent outlet cone which guide the flow to the continuation of the pipe. The throat is the union of the two cones and is the narrowest part of the tube. The high-pressure outlet is connected at the beginning of the inlet cone. This shot is average since it is obtained for several perforations around the tube, this set of connections is called piezometric ring, equivalent to the triple T configuration mentioned in the orifice plates. The low-pressure outlet is placed in the throat of the tube and can also be made piezo metrically. The output cone is said to be a recovery because it recovers to a certain extent a large percentage of the pressure drop caused by the restriction.
When a fluid such as water or air passes through a narrowing, the static pressure decreases, this effect is used to measure the speed of the liquids, to atomize liquids (spray), to make the vacuum. Both the venturi tube and the pitot tube can be used for liquids and gases, however, in practice, the venturi tube is used mainly for liquids while the pitot tube is preferably used for gases.

Other applications of the Venturi Tube
Aeronautics
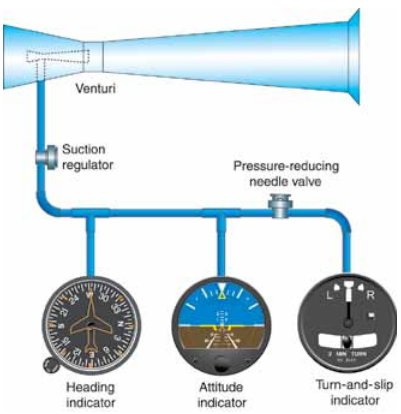
It intervenes in effects related to the viscosity of the air that can be explained by the Navier-Stokes equations. In addition, a Venturi tube is used to provide suction to instruments that work with vacuum (Turn Coordinator, Artificial Horizon) in aircraft that are not equipped with mechanical vacuum pumps. Although the Venturi effect is often used to explain the lift produced on aircraft wings, this effect can not really explain airborne lift, because an alar profile does not act like a Venturi tube accelerating the air particles: the particles are accelerated due to the conservation of energy (explained by Bernoulli's principle, by virtue of which air acquires greater speed when passing through the convex region of an airplane's wing), conservation of momentum (Newton's third law is used for explanation) and mass (Euler equations are used).
In the Automotive Industry
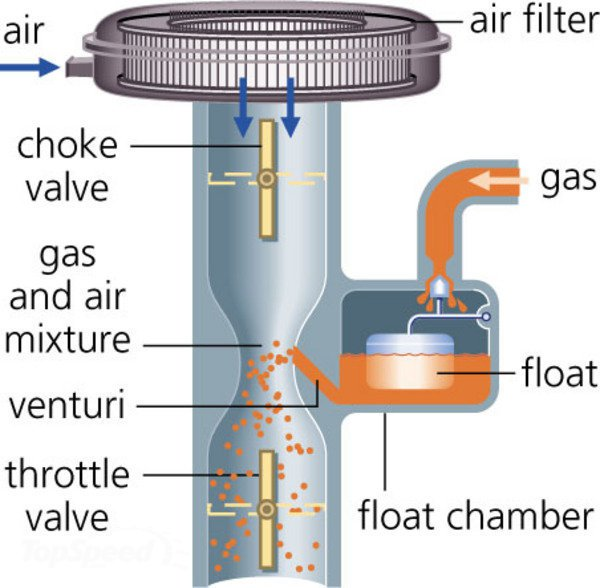
In the car's carburetor, the use of this can be observed in what is Fuel Fuel. The engines require air and fuel to operate. A liter of gasoline needs approximately 10,000 liters of air to burn, and there must be some metering mechanism that allows the mixture to enter the engine in the correct proportion. This dose is called a carburetor, and is based on the Venturi principle: by varying the inside diameter of a pipe, the speed of the air passage is increased. The Venturi Tube allows the mixing of the air with the fuel to be combustion, without which the engine of the car could not start, hence the principle of this tube is used as an important part of the automotive industry. The Venturi effect in the carburetor consists of passing a current of air at high speed, caused by the descent of the piston by a quantity of gasoline that is feeding through a tank forming a gaseous mass. The richness of the gasoline depends on the diameter of the spout.
Household
In the water ozonator equipment, a small Venturi tube is used to suck the ozone that is produced in a glass tank, and thus mix it with the flow of water that leaves the equipment with the idea of destroying the possible pathogenic bacteria and to deactivate viruses and other microorganisms that are not sensitive to chlorine disinfection. Also in irrigation systems of our houses is a Venturi pipe.
