Introduction
Nanotechnology, a term that sounds like it belongs in a science fiction novel, is actually a fascinating field with real-world applications that impact our lives in more ways than we realize.
It’s the reality humming beneath the surface of your touchscreen, the unseen hero in medical breakthroughs, and the future architect of cleaner environments.
Whether you’re nine or ninety, understanding nanotechnology is like peeking behind the curtain of tomorrow’s magic.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
What is Nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology deals with the manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular scale. That’s incredibly tiny – a nanometer (nm) is one-billionth of a meter, roughly the width of a few atoms! At this scale, materials behave differently than they do in our everyday world.
Scientists are harnessing these unique properties to create new materials and devices with incredible capabilities.
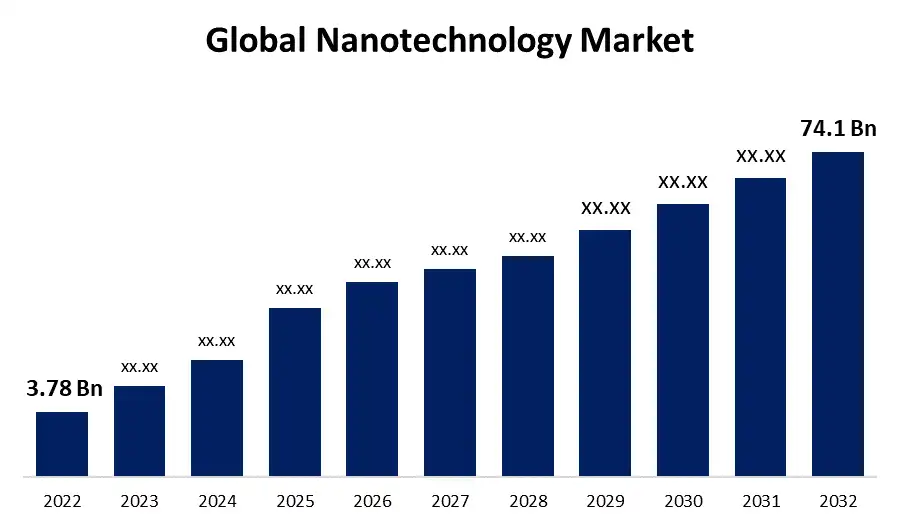
The global nanotechnology market is expected to reach a staggering $74.1 billion by 2032. It is highlighting the immense potential and rapid growth of this field. But what can we expect from this microscopic revolution?
Read More:How AMD MI300X is A Game-Changer in the AI Hardware Landscape – techovedas
Applications and Innovations
Nanotechnology is steering the world towards radical transformations.
In medicine, nanoparticles are being designed to target cancer cells with precision, sparing patients from the collateral damage of chemotherapy.
Electronics are becoming faster, smaller, and more efficient, thanks to nano-sized transistors.
The energy sector is buzzing with the potential of nanotechnology. Nano-coatings improve the efficiency of solar cells and wind turbines, making renewable energy sources more viable and accessible.
Meanwhile, environmental applications are equally groundbreaking. Nanotechnology is at the forefront of water purification systems, enabling the removal of even the tiniest contaminants to provide safe drinking water for millions.
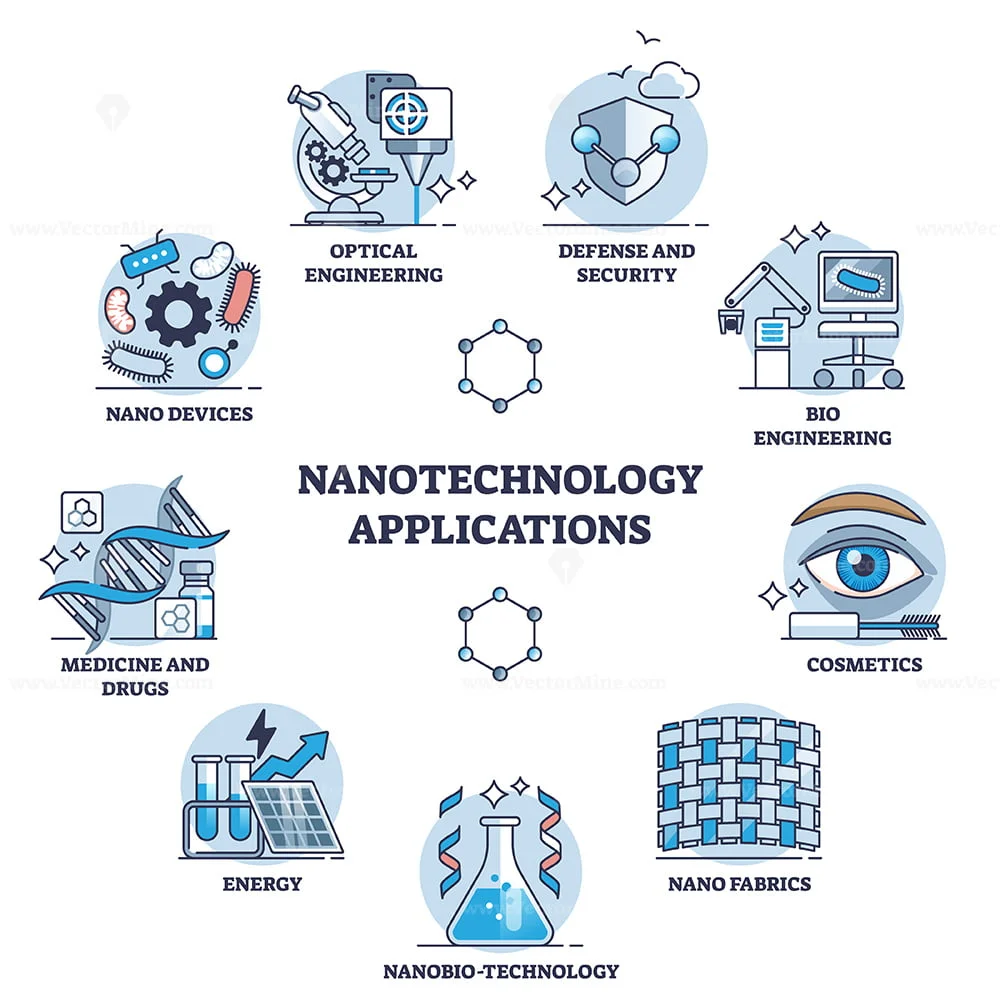
One lesser-known application of nanotechnology is in textiles, where nanoparticles are creating fabrics that repel water, stains, and even bacteria, revolutionizing the fashion and healthcare industries.
Equally intriguing are the implications for food science, where nano-encapsulation ensures nutrients are delivered more efficiently, enhancing food’s nutritional value without altering taste or appearance. This stealthy application promises a new era of fortified foods, fighting malnutrition on a global scale.
Read More: Elon Musk Announces Open-Source Release of Grok – techovedas
Nanotech’s Role in AI Hardware
AI systems are power-hungry, requiring significant computational resources to process and analyze vast datasets. Traditional silicon-based chips, which have been the backbone of computing for decades, are nearing their physical and operational limits.
They can only get so small and so fast before they hit a wall in terms of heat management and transistor density.
Read More:How Can We Make 3D chips Using 2D materials? – techovedas
Nanotechnology offers a solution to this impasse. It allows for the engineering of materials and components at the atomic and molecular levels, which is the scale of nanometers (one billionth of a meter). At this scale, materials can exhibit unique electrical, optical, and magnetic properties that are not present in their bulk form.
By leveraging these unique properties, nanotechnology can create ultra-dense memory and processors. This means packing more transistors into a chip without increasing its physical size, leading to greater processing power and storage capacity. For AI, this translates to:
- Faster Learning: AI algorithms can process more data in less time, improving their ability to learn from data patterns and make predictions.
- Quicker Computation: With more transistors working in parallel, AI can perform complex calculations at a much faster rate.
- Unprecedented Efficiency: Nanotech-enabled hardware can operate at lower power levels, reducing energy consumption while maintaining high performance.
Read More: Read More: Intel CPU Dominance in Q4 2023: Shipping 50 million Units, over 3 Times AMD & Apple Combined – techovedas
Conclusion
Nanotechnology offers a glimpse into a future where the impossible becomes possible. It’s a field brimming with potential, with the power to revolutionize everything from healthcare to energy production. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. As we delve deeper into the world of the ultra-small, we can be sure that nanotechnology will continue to shrink limitations and expand our possibilities.



