A Blueprint for Network Communication || OSI Reference Model
Introduction:
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model serves as a crucial blueprint for network communication, providing a structured framework for understanding how different protocols and technologies interact. By breaking down the complex process into seven distinct layers, the OSI model simplifies network design, troubleshooting, and interoperability. Let's delve into how the OSI model works and explore the functionality of each layer.
Layers of the OSI Model:
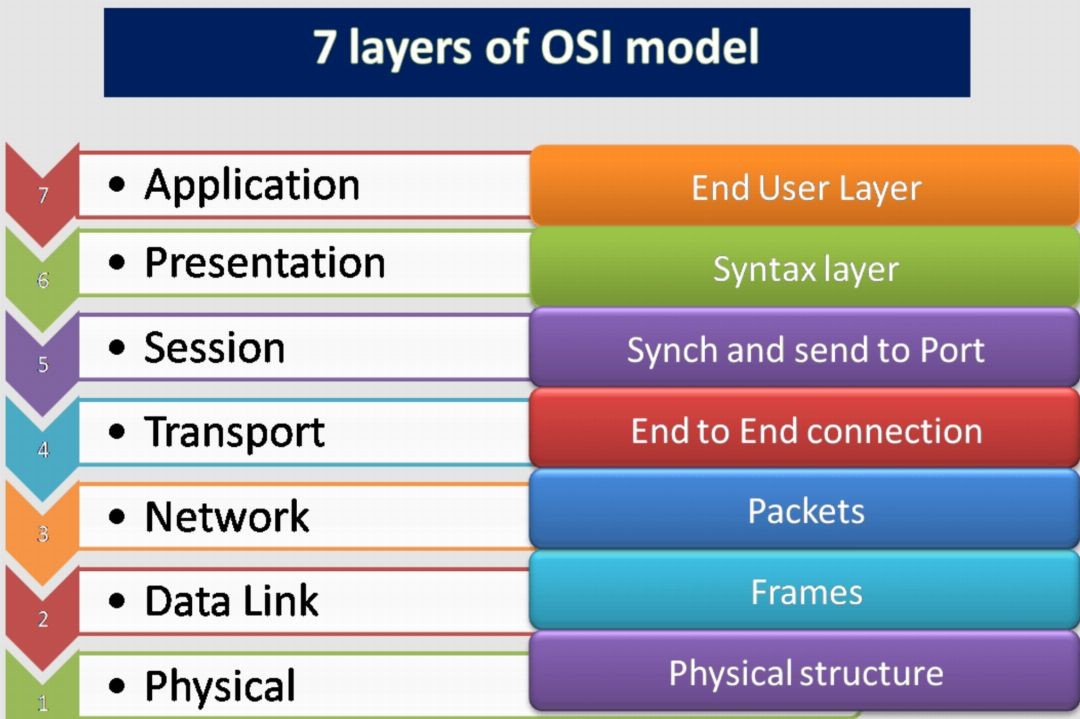
1.Physical Layer:
The Physical layer is responsible for transmitting raw data bits over the physical medium, such as wires or wireless signals. It defines characteristics like voltage levels, cable specifications, and data transmission rates.
2. Data Link Layer:
The Data Link layer ensures reliable and error-free transmission of data frames between directly connected devices. It adds necessary framing, performs error detection, and controls flow to avoid overwhelming the recipient.
3.Network Layer:
The Network layer enables the routing of data packets across multiple networks. It determines the optimal path for data transmission, handles addressing, and manages network congestion.
4. Transport Layer:
The Transport layer establishes end-to-end communication between applications. It segments data from the upper layers into manageable units, adds sequencing and error-checking information, and provides reliable delivery of data.
5. Session Layer:
The Session layer establishes and manages communication sessions between applications. It handles session setup, synchronization, and termination, ensuring secure and orderly data exchange.
6. Presentation Layer:
The Presentation layer focuses on data representation and ensures that data exchanged between systems can be interpreted correctly. It handles tasks such as data compression, encryption, and data format conversion.
7. Application Layer:
The Application layer interacts directly with end-users and provides services for applications. It enables communication with network services like email, web browsing, file transfer, and remote access.
Interactions between Layers:
The beauty of the OSI model lies in its layered approach, where each layer relies on the services provided by the layer below it while providing services to the layer above it. This modular design allows for easy troubleshooting, scalability, and interoperability. Data flows sequentially through the layers, with each layer adding its necessary functions to facilitate reliable and efficient communication.
Benefits and Importance:
The OSI model serves as a universal guideline for network architects and developers. It ensures that different networking technologies can seamlessly communicate with each other, fostering interoperability and standardization. By following the principles of the OSI model, network professionals can design, implement, and troubleshoot complex networks with ease. It provides a common language and reference point for networking discussions and fosters collaboration among industry professionals.